
1 The Enfield Local Development Scheme, submitted to the Secretary of State for approval and adopted by the Council in 2010, proposes that in the three year period from 2009 to 2012, the Council will produce the following Local Development Documents:
2 The Core Strategy will set out the vision for the future development of the Borough and the core policies for delivering this vision.
3 The Proposals Map will identify:
4 The Sites Schedule will set out any land that has been allocated for specific types of development.
5 The Enfield Design Guide will reinforce the Council’s commitment to good design, promoting an urban and rural design framework to raise standards and inspire good design.
6 The Development Management Document will set out standards to guide and control new development and land use change in Enfield. Responses received on the Issues and Options Report highlighted a need to reconsider whether this document should in fact be prepared as a development plan document (DPD) rather than a supplementary planning document (SPD) as set out in the LDS. The Council now intends to bring this document forward as a DPD.
7 Area Action Plans will be drawn up for North East Enfield, the Central Leeside Area, Enfield Town and the area around the North Circular Road in the south-east of the Borough. These are areas where proposals for change are concentrated and where land uses and activities are particularly complex. As such, these areas would benefit from more detailed scrutiny and the preparation of planning frameworks to resolve conflicting objectives, deliver planned growth, protect areas sensitive to change and stimulate regeneration.
8 The North London Joint Waste DPD will be prepared jointly by the member boroughs of the North London Waste Authority to set out planning policies for waste disposal facilities and sites.
9 Masterplans for the Place Shaping Priority Areas will sit within the planning framework of the Core Strategy and Area Action Plans, and will be adopted as SPDs within the LDF. Preparation of the Masterplans has commenced and they are being prepared to provide detailed development guidance to areas that have particular constraints and opportunities, and will contribute greatly to the immediate area and Borough in terms of housing, employment and services.
10 Both the S106 SPD and at a future stage the introduction of a Planning Obligations and Community Infrastructure Levy SPD will detail the Council's approach to Planning Obligations and the Community Infrastructure Levy, including a schedule of charging rates.
11 The Core Strategy is the key Local Development Document (LDD); it contains the Council’s vision and core policies and links to other LDDs in the following ways:-
12 LDF documents can be viewed on the Council's website at www.enfield.gov.uk/ldf.
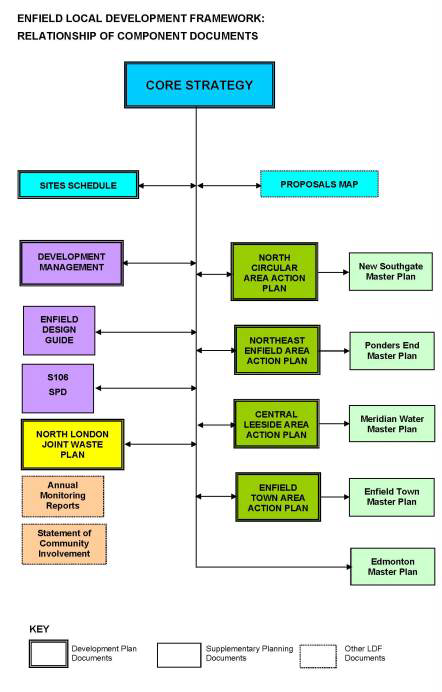
Table 2.1 Relationship of Core Polices & Saved UDP Policies
UDP POLICY |
LDF POLICY DOCUMENTS |
||||||
UDP Policy Policy Title |
Policy Title |
Is the UDP Policy superseded by this DPD Or Expired1 |
Core Strategy |
Development Management DPD |
Area Action Plan DPDs |
Sites Schedule DPD |
Enfield Design Guide SPD |
(I) EO1 |
Equal Opportunities |
Y |
92 |
|
|
|
|
(I) N1-N4 |
Borough Structure |
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
(I)EN1-EN6 |
General Environmental Considerations |
Y |
28-36 |
|
|
|
|
(II)EN3-EN5 |
Advertisements |
|
33 |
Y |
|
|
Y |
(II) EN6 |
Telecommunications |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) EN10-EN15 |
Nature Conservation |
Y |
36 |
|
|
|
|
(II) EN16 |
Article 4 Directions |
Expired |
|
|
|
|
|
(II) EN17-EN18 |
Environmental |
Y |
29 |
|
|
|
|
(II) EN20-EN21 |
Vacant and under-used land |
Expired |
|
|
|
|
|
(II) EN23 |
Environmental Education |
Expired |
|
|
|
|
|
(II) EN24-EN26 |
Minerals |
Y |
23 |
|
|
|
|
(II) EN29 |
Waste |
Y |
21, 22 |
|
|
|
|
(II) EN30-EN32 |
Pollution |
Y |
32 |
|
|
|
|
(I) G1-G3 |
Green Belt |
Y |
33 |
|
|
|
|
(II) G1-G5 |
Environmental Measures / |
Y |
33 |
|
|
|
|
(II) G6 |
Areas of Special Character |
Y |
33 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G7-G10 |
Landscape Measures |
|
31 |
Y |
|
|
Y |
(II) G11-G19 |
Environmental Measures affecting New Development |
|
28, 29 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G20-G21 |
Urban Edge |
|
33 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G22 & G24 |
Agriculture |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G25 |
Horticulture |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G26 |
Garden Centres |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G27-G28 |
Horsekeeping |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G29-G30 |
Lee Valley Regional Park |
Y |
33, 35 |
|
|
|
|
(II) G31-G33 |
Recreation |
Y |
11, 34 |
|
|
|
|
(II) G34-G39 |
Residential Development |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G40-G41 |
Horticulture / Garden Centres |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(11) G42 |
Livestock Units |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G43 |
Horsekeeping |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) G44-G45 |
Landscape Treatment |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(I) O1, O2 & |
Open Space & Metropolitan Open |
Y |
34 |
|
|
|
|
(1) O3 |
Green Chains |
|
34 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) O1-O5 |
Metropolitan Open Land |
Y |
34 |
|
|
|
|
(II) O6-O9 |
Green Chains |
|
34 |
Y |
|
|
|
(11) O10-O18 |
Urban Open Space |
Y |
34 |
|
|
|
|
(II) O19 |
Playing Fields |
Y |
34 |
|
|
|
|
(II) O20 |
Leisure Gardens (Allotments) |
Y |
34 |
|
|
|
|
(I)C1 |
Conservation and Townscape |
Y |
31 |
|
|
|
|
(II)C1-C7 |
Archaeology and Ancient Monuments |
Y |
31 |
|
|
|
|
(II) C8-C11 |
Procedures |
Expired |
|
|
|
|
|
(II) C12-C14 |
Protection and Maintenance of Listed Buildings |
Y |
31 |
|
|
|
Y |
(II) C16-C17 |
Use of Listed Buildings |
|
31 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) C18-C20 |
Historic Landscapes |
|
31 |
Y |
|
|
Y |
(II) C21 |
Designation of Conservation Areas |
Y |
31 |
|
|
|
|
(II) C23-C25 |
Safeguarding the Environment in Conservation Areas |
Y |
31 |
|
|
|
|
(II) C26-C31 |
Quality of Development |
30, 31 |
Y |
|
|
|
|
(II) C32-C34 |
Advertisements |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) C35-39 |
Tree Protection |
|
|
Y |
|
Y |
|
(I) GD1-GD2 |
General |
Y |
30 7 |
|
|
|
|
(II) GD1 |
Land Use Compatibility |
Expired |
|
|
|
|
|
(II) GD3 - GD9 |
Planning Standards |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) GD 10 |
Integration of |
Y |
30 |
|
|
|
|
(II) GD12-GD13 |
Flooding and Surface Water Drainage |
Y |
28, 29 |
|
|
|
|
(I) H2-H4 |
Housing |
Y |
2 - 6 |
|
|
|
|
(II) H2-H4 |
Housing - The Existing Housing Stock |
|
4-6 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) H5-H6 |
Housing - The Existing Housing Stock |
Y |
5-6 |
|
|
|
|
(II) H8-H15 |
Standards of Residential Development -General Standards |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) H16 |
Standards of Residential Development -Conversions |
|
|
Y |
|
|
Y |
(II) H18 |
Standards of Residential Development -Housing Needs of People with Disabilities |
|
6 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) H2O |
Housing Support Services -Accommodation for Homeless Persons |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) H22 |
Housing Support Services - Special Needs |
Y |
6 |
|
|
|
|
(I) El-E4 |
Employment and Economic Development |
Y |
12 |
|
|
|
|
(II) El |
Availability of Land and Labour |
Y |
13, 14 |
|
|
|
|
(II) E2-E3 |
Commercial and Industrial Defined Areas |
Y |
14 |
|
|
|
|
(II) E4 |
Special Needs of Small Firms |
|
15 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) E5-E7 |
Secondary Industrial Premises |
Y |
14, 15 |
|
|
|
|
(II) E9 |
Non-Commercial and Industrial Uses |
|
14 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) E11 |
Standards of Development |
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
(II) E12 |
Infrastructure |
Expired |
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) E13 |
Infrastructure |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) E14-E15 |
Environmental Safeguards |
|
|
Y |
Y |
|
|
(I) S1-S3 |
Shopping and Town Centres |
Y |
17 |
|
|
|
|
(II) S1 |
Town Centres |
Y |
17 |
|
|
|
|
(II) S2 |
Town Centres |
Y |
17 |
|
|
|
|
(II) S3 |
Management of the Town Centres |
|
17, 18 |
Y |
Y |
|
|
(II) S5-S11 |
Non-Retail Uses in Town Centres |
|
17, 18 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) S13-S15 |
Local Centres |
|
17, 18 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) S17 |
Major Out-of-Centre |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) S18 |
Food and Drink |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) S19 |
Design Considerations |
|
30 |
|
|
|
Y |
(II) S20-S21 |
Accommodation on Upper Floors |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) S22 |
Access for People with Disabilities |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(I) T1-T11 |
Transportation |
Y |
24 - 27 |
Y |
|
|
|
(II) T1 |
Land Use and Transportation |
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
(II) T3-T5 |
Public Transport |
Y |
26 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T6-T7 |
Roads - Highway Network |
Y |
24 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T8-T12 |
Roads - Environmental Considerations |
Y |
24-27 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T13 |
Roads - Highway Improvements |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) T14 |
Roads - Highway Improvements |
Y |
46 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T15 -T17 |
Pedestrians |
Y |
25 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T19-T21 |
Cycling |
Y |
25 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T22-T23 |
Freight - Road Freight |
Y |
27 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T24 |
Freight - Rail |
Y |
27 |
|
|
|
|
(II) T25-T26 |
Freight - Waterways |
Y |
27 |
|
Y |
|
|
(II) T27-T32 |
Parking |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) T33 |
Safety |
|
9 |
Y |
|
|
|
(I) AR1-AR2 |
Arts, Recreation and Tourism |
Y |
11, 12 |
|
|
|
|
(II) AR1& AR3 |
Recreation |
Y |
11 |
|
|
|
|
(II) AR4-AR5 |
Arts, Culture and Entertainment |
Y |
11 |
|
|
|
|
(II) AR6-AR7 |
Tourism |
Y |
12 |
|
|
|
|
(I) CS1 |
Community Services |
Y |
7 - 10 |
|
|
|
|
(II) CS1-CS3 |
Land and Environmental Considerations |
|
|
Y |
|
Y |
|
(II) CS4 |
Day Nurseries |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) CS5 |
Places of Public Worship |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
(II) ET1 |
Enfield Town - Land Uses |
Y |
17, 18, 42, 43 |
|
|
|
|
(II) ET3-ET15 |
Enfield Town - Shopping Developments |
Y |
17, 18, 42, 43 |
|
|
|
|
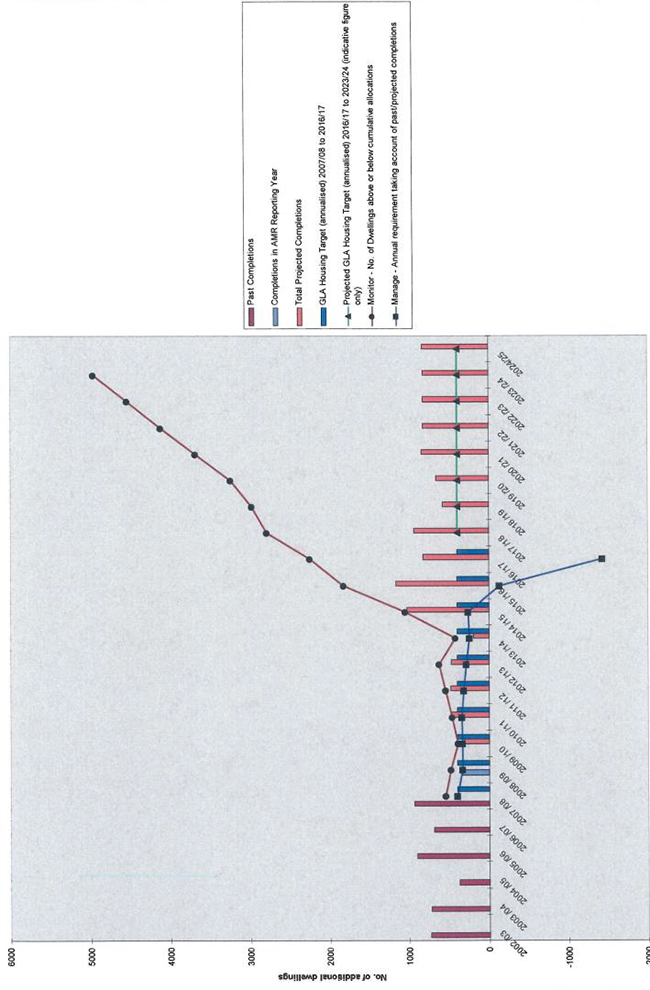
Picture 3.1 Housing Trajectory 2010/11 - 2024/25
National Planning Policy
1 The Department for Communities and Local Government prepares Planning Policy Guidance Notes (PPGs) and Planning Policy Statements (PPSs) to provide guidance on UK planning policy. National planning policies, guidance and circulars that have informed the Core Strategy are listed below and are available to download at: http://www.communities.gov.uk.
2 Plans, guidance and strategies produced by other government departments and advisory bodies such as the Department of Health, the Department for Children, Schools and Families, the Home Office, English Heritage and the Commission for Architecture and the Built Environment (CABE) have also informed the preparation of the Core Strategy.
Regional Plans and Strategies
3 The Core Strategy has been prepared having regard to regional plans and policies produced by the Greater London Authority, London Development Agency, North London Strategic Alliance and other bodies, including:
4 Lee Valley Regional Park Plan, Lee Valley Regional Park Authority (2000)
5 London Plan, Greater London Authority (2008)
6 London Plan Supplementary Planning Guidance (SPG) -
7 London Plan Best Practice Guidance (BPG)
8 A New Plan for London, Greater London Authority (2009)
9 Mayors Transport Strategy Statement of Intent, Greater London Authority (2009)
10 Rising to the Challenge, Proposals for the Mayors Economic Development Strategy for Greater London, Greater London Authority (2009)
11 North London Joint Waste Strategy 2004-2020
12 Sub Regional Development Framework – North London, Greater London Authority (2006)
13 North London Development Investment Framework, London Development Agency (2008)
14 London Stansted Cambridge Growth Corridor, Greater London Authority (2004)
15 Thames Catchment Flood Management Plan, Environment Agency (2008)
16 Upper Lee Valley Vision, North London Strategic Alliance (2007)
Other plans and strategies of the Council and its partners
17 Various plans and policies produced by the Council and its partners have also informed the Core Strategy. Those with spatial implications which inform the LDF include:
18 Community Cohesion Strategy 2007 – 2009, Enfield Council (2007)
19 Community Safety Strategy 2005 – 2008, Enfield Council (2005)
20 Enfield’s Future: A Sustainable Community Strategy for Enfield 2007 - 2017 – Enfield Strategic Partnership (2007)
21 Place Shaping Strategy, Enfield Council (2008)
22 Building Futures, Changing Lives: Enfield’s Local Area Agreement, Enfield Council (2009)
23 Choosing Health in Enfield 2007/08, Enfield PCT (2007)
24 Making Enfield Better, Draft Primary Care Strategy, Enfield NHS Primary Care Trust (2009)
25 Local Health Delivery Plan (Enfield, Barnet & Haringey PCT)
26 Health Improvement Action Plan, Enfield, Barnet & Haringey PCT (2005 – 2008)
27 Developing Primary and Community Services Over The Next Five Years, Enfield, Barnet & Haringey PCT (2006)
28 Everybody Active: Enfield Sport, Physical Activity and Physical Education Strategy 2009 – 2014, Enfield Council (2009)
29 Enfield's Library Strategy and Development Plan 2007 - 2012
30 Enfield's Homelessness Strategy (2008)
31 Enfield's Action Plan for Tackling Overcrowding (2009)
32 Children and Young People’s Plan 2009 – 2012, Enfield Council (2009)
33 Enfield’s Older People Strategy 2005 – 2010, Enfield Council (2005)
34 Enfield Safer and Stronger Communities Board Partnership Plan 2009-2012 (2009)
35 Enriching Enfield: Enfield's Culture and Leisure Strategy 2005 - 2008, Enfield Council (2005)
36 Creative Enfield: Enfield’s Arts and Creativity Strategy 2009 - 2013
37 Housing Strategy 2005 - 2010 – Enfield Council (2005)
38 Local Implementation Plan, Enfield Council (2007)
39 Enfield Skills and Employment Strategy 2008 – 2011, Enfield Strategic Partnership (2008)
40 Unitary Development Plan, Enfield Council (1994)
41 Air Quality Action Plan 2003
42 Enfield Heritage Strategy 2008
43 London Borough of Enfield Draft Multi-Agency Emergency Flood Plan (2009)
44 Many of the above documents have shorter time horizons than the Core Strategy. Subsequent iterations will be monitored through the Annual Monitoring Report and future reviews of the Core Strategy will be brought forward as necessary.
Evidence Base
45 In preparing the Core Strategy it has been necessary to have a detailed understanding of the issues facing the Borough. The information to inform this analysis is known as the Evidence Base and is subject to a continuing process of revisions and updating. The documents are available via the Council's Core Strategy web page: http://www.enfield.gov.uk/core-strategy. The following supporting technical documents form part of the evidence base for the Core Strategy:
Table 5.1 Key Developments and Policies in Adjoining Boroughs
Information Source |
Relevant Policies and Developments |
Cross Borough Implications |
East of England |
||
The East of England Plan (EEP) is the regional plan providing strategic direction for the local councils adjoining Enfield to the north and north east. |
Harlow is identified as an area for the concentration of new development with a minimum of 16,000 housing units are to be provided (including areas of East Hertfordshire and Epping Forest) to 2021. |
Significant growth at Harlow may have implications particularly with regard to the London-Stansted-Cambridge-Peterborough corridor in terms of the scale of development, public transport implications and linkages with the London element of the Growth Area. |
Borough of Broxborne |
|
|
East of England Plan |
Although not identified as a strategic centre for housing growth within the EEP, it is located within the London Arc Sub Region, with a minimum housing target of 5,600 dwellings. |
N/A |
Core Strategy Consultation Document (Nov. 2008) |
The accommodation of new housing growth is provided for in existing urban areas, with the key development site of Greater Brookfield identified for housing growth to 2021. Beyond this to 2031, areas at Cheshunt, Hoddesdon and Goffs Laneare identified as areas of search for suitable sites for housing growth. |
Development within the south of the Borough and within the Lee Valley Regional Plans will have implications for public transport improvements, traffic issues and infrastructure provision. |
Epping Forest District Council |
|
|
East of England Plan |
The EEP identifies a minimum housing provision of 3,500 dwellings in Epping Forest. |
N/A |
Core Strategy Issues and Options document due for publication in Spring 2010. |
N/A |
N/A |
Hertsmere Borough Council |
|
|
East of England Plan |
The EEP identifies a housing target of 5,000 new dwellings for Hertsmere. |
N/A |
Core Strategy Submission 2009 (Withdrawn) |
New development will be accommodated at Borehamwood, Potters Bar and Bushey. The three locations are identified as Strategic Housing Locations, and up to 30 per cent of new housing will be provided at Potters Bar. Borehamwood and Potters Bar will remain the two largest centres for employment in the Borough. |
Cross boundary issues include infrastructure provision, traffic congestion and viability of nearby town centres as Potters Bar is situated in the east of the Borough adjacent to Enfield's north west boundary. |
Welwyn Hatfield Borough Council |
|
|
East of England Plan |
Provisions of the EEP related to Welwyn Garden City and Hatfield are under review following a successful legal challenge related to the housing figures for Welwyn Hatfield and the need for a Green Belt review. |
N/A |
Core Strategy Issues and Options (March 2009) |
Issues and options for future growth are presented however, future development locations and housing numbers are not are conclusive and are subject to discussion with the Cabinet Office following the successful legal challenge to the EEP. |
N/A |
London Borough of Barnet |
||
London Plan |
The London Plan identifies Brent Cross, Cricklewood and West Hendon as an Opportunity Area, and Mill Hill East as an Area for Intensification. The London Plan also contains proposals for phasing improvements to the A406, and improvements to the Northern and Piccadilly underground. The London Plan's |
N/A |
Core Strategy Issues and Options (June 2008) |
Development will predominantly take place in the western part of the Borough at Brent Cross, Colindale and Mill Hill East. |
Southgate and Cockfosters centres, in Enfield, are close to the Barnet boundary, and the area around North Circular Roadis identified as a Strategic Growth Area, for which an AAP is under preparation. |
Colindale AAP |
The AAP provides for the development of 10,000 new homes and 1,000 new jobs. |
As above |
Mill Hill East AAP |
The AAP provides for 2,000 new homes and 500 new jobs at Mill Hill East. |
As above |
London Borough of Haringey |
||
London Plan |
Haringey Heartlands/ Wood Green is designated in the London Plan as an Area of Intensification. |
N/A |
Haringey Heartlands Development Framework SPD |
Proposals for the creation of approximately 1,500 new jobs and 1,700 new homes are provided for as part of an intensive mixed use redevelopment. A Haringey Heartlands Development Framework SPD is in place to guide development in the area. |
Implications may arise on Enfield's south west boundary, at the North Circular Road and New Southgate, where a coordinated approach could address the potential transport issues and the delivery of education and community facilities through a joint approach. |
Tottenham Hale Urban Centre Masterplan SPD |
Of the new jobs and accommodation to be provided in the Upper Lee Valley, 5,000 jobs and over 1,000 new homes are to be provided at Tottenham Hale. The Tottenham Hale Urban Centre Masterplan is in place to guide development in the area. |
Development proposed within the UpperLeeValley at Tottenham and Central Leeside will have implications for Central Leeside and Meridian Water, particularly in terms of infrastructure, transport and access, economic opportunities, and the cumulative impact of growth in the UpperLeeValley. |
Core StrategyProposed Submission 2010 |
Tottenham Hale and Haringey Heartlands are identified as the key growth areas, where future growth will be directed. |
Development proposed in Haringey, in particular in the Northumberland Park area (which relates most closely to the Enfield border) will have cross borough issues in terms of the transport network, and in the provision of green, community and physical infrastructure, for which a co-ordinated approach will enable the timely and efficient delivery of development, infrastructure and services. |
London Borough of Waltham Forest |
||
London Plan |
WalthamForest adjoins the eastern boundary of Enfield along the UpperLeeValley, which, as described above, is identified as an Opportunity Area, within the London Plan. |
N/A |
Core Strategy Preferred Options January 2010 |
The Core Strategy Preferred Options Report was published in January 2010 and states that the focus for future development will be Blackhorse Lane, Walthamstow Town Centre, and the Northern Olympic Fringe. |
Industrial development, employment growth and release of employment land in the west of the Borough may have implications for Central Leeside and the Meridian Water site in terms of economic opportunities and the provision of infrastructure. |
The Black Horse Lane Interim Planning Policy Framework (September 2006) |
Provides for the creation of a new centre around Blackhorse Roadstation, and the provision of 2,000 new homes, and 1,000 new jobs in the area. |
Development may have implications for the transport network, in particular east west movements on the North Circular Road, and in terms of cumulative impacts of development within the Upper Lee Valley. |
Walthamstow Interim Planning Policy Framework (May 2008) |
This will form the interim planning policy for the area to be covered by an AAP for Walthamstow that is identified for production. The Framework makes provision for 2,438 new homes and local improvements to transport infrastructure. |
N/A |
Table 6.1 Key Issues, Strategic Objectives and Core Policies
Key Issue |
Strategic Objective |
Core Policy |
1 |
1 |
CP1, CP 37 - 45 |
2 |
4 |
CP 2- 6 |
3 |
6, 7 |
CP 12 - 19 |
4 |
3, 5 |
CP 7 - 9 |
5 |
3 |
CP 7 -11 |
6 |
7 |
CP 8, CP 9, CP 39 |
7 |
3 |
CP 9 |
8 |
9 |
CP 33 - 35 |
9 |
3, 6 |
CP 26, CP 35, CP 37, 38, 40, 41 |
10 |
8 |
CP 24 - 27 |
11 |
9, 10 |
CP 30, CP 44, 45 |
12 |
2, 8 |
CP 24 - 27 |
13 |
2 |
CP 20 - 22, CP 28 - 30, CP 32, CP 36 |
14 |
10 |
CP 30 - 31 |
15 |
2 |
CP 21 & CP 32 |
The Core Strategy is accompanied by a Proposals Map which illustrates:
The following table provides explanation on these changes and in effect helps identify the link between extant UDP designations and new designations introduced by this Core Strategy.
Table 7.1 Link between extant UDP designations and new designations.
Core Strategy Designation |
(UDP) Designation |
Type of Change |
Notes |
Major Centres |
Town Centre (Enfield) |
New designation |
London Plan (introduced since UDP) classifies Enfield as a 'major centre'. Council plans are required to reflect this. |
District Centres |
Town Centre (Edmonton Green, Angel Edmonton, Palmers Green & Southgate) |
New designation |
London Plan (introduced since UDP) classifies Edmonton Green, Upper Edmonton, Palmers Green & Southgate as 'district centres'. Council plans are required to reflect this. |
Primary Shopping Frontage |
Town Centre (Enfield) |
New designation — consists of 'core retail frontages' in UDP and additional retail frontages identified as identified in 2007 & 2009 retail study. |
As required by Planning Policy Statement 4. |
Strategic Industrial Land |
Primary Industrial Area |
New designation. Largely the same as primary industrial areas but numerous minor adjustments to make boundary consistent with actual landuses. |
Reflects the London Plan identification of 'preferred industrial locations' |
Locally significant industrial sites |
--- |
New designation |
Reflects the need to protect the borough's supply of industrial employment on land not identified by the London Plan as `preferred industrial locations' |
Green belt |
Green belt |
Main area of strategic change to Greenbelt is Enfield Island. |
The area of residential redevelopment undertaken at Enfield Island in the 1990s has been excised from the Greenbelt. Various areas added to the borough through the 1994 boundary changes are Greenbelt (these were already designated as Greenbelt when in previous boroughs/districts, so these changes are not strategic). Also minor map changes which have not changed the map on the ground, arising from more accurate mapping. |
Major |
--- |
New designation |
Acknowledges the presence of such development whilst reinforcing the fact that such development remains subject to the objectives of the Greenbelt. |
Metropolitan open land |
Metropolitan open land |
Additions to MOL proposed in UDP Interim Amendment June 1997 |
These additions were adopted as Council policy but did not proceed to come into effect. The Core Strategy now gives these additions legal effect. |
Open Spaces (Public and Private) |
--- |
New designation |
This designation recognises the strategic importance of the network of these areas throughout the Borough. |
Conservation areas |
Non plan |
Post UDP |
Proposals map therefore show areas as they now stand. |
Area subject to article 4 Direction |
Non plan |
Post UDP |
On-line proposals map show areas as they now stand. |
Sites of metropolitan importance for nature |
Sites of nature conservation importance |
New designation (formerly part of UDP sites of nature |
Since the UDP sites of nature conservation importance have been divided into metropolitan and borough sites of importance for nature conservation. |
Sites of borough importance for nature |
Sites of nature conservation importance |
New designation (formerly part of UDP sites of nature |
Since the UDP sites of nature conservation importance have been divided into metropolitan and borough sites of importance for nature conservation. |
Locations of area action plans |
--- |
New designation |
Areas identified by the Council as part of its strategic directions as set out in Enfield's Future — A Sustainable Strategy for Enfield 2007-2017 (Enfield Strategic Partnership) |
Place shaping priority areas |
--- |
New designation |
Areas identified by the Council as part of its strategic directions as set out in Enfield's Future — A Sustainable Strategy for Enfield 2007-2017 (Enfield Strategic Partnership) |
Table 8.1 Glossary
Word |
Description |
Accessibility |
The ability of people, including elderly and disabled people, those with young children and those encumbered with luggage or shopping, to move around an area and reach places and facilities. |
The Act |
The Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004, as amended by the Town and Country Planning (Local Development) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2008. |
Adoption |
The stage of the adoption process at which the local planning authority can adopt, by resolution of the Council, local development documents as Council policy. |
Adoption Process |
The statutory process by which a local planning authority prepares, publishes and formally adopts a local development document which is also a development plan document. |
Affordability |
A measure of whether housing can be afforded by certain groups of households. The terms affordability and affordable housing have different meanings. |
Affordable Housing |
Housing intended to meet the needs of eligible households including availability at a cost low enough for them to afford to purchase, with the price being determined with regard to local incomes and local house prices. Affordable housing is divided into social rented housing and intermediate housing. The terms affordability and affordable housing have different meanings. |
Aggregates |
Sand, gravel, crushed rock and other bulk materials obtained by quarrying or similar methods and used by the construction industry. |
Air Quality Management Area |
Since 1997 local planning authorities have been carrying out a review and assessment of air quality on their area. The aim of the review is to assist authorities in carrying out their statutory duty to work towards meeting the national air quality objectives. If a local authority finds any places where the objectives are not likely to be achieved, it must declare an Air Quality Management Area there. |
Annual Monitoring Report |
Part of the local development framework which measures and assesses the implementation of the local development scheme and the extent to which policies in local development documents are being successfully implemented. Also known as an AMR. |
Area Action Plan |
A local development document (which is also a development plan document) which sets out a strategy for the planning of areas having a concentration of proposals for change or where land uses and activities and planning issues are particularly complex. Also known as an AAP. |
Area Designation |
An area identified on the proposals map within which certain core policies apply. |
Area for Regeneration |
An area constituting a borough ward in particular socio-economic need, defined on the basis of the index of the 20% most deprived wards in London. |
Area of Special Advert Control |
Area of Special Advert Control is an area specifically defined by the local planning authority because they consider that its scenic, historical, architectural or cultural features are so significant that a stricter degree of advertisement control is justified in order to conserve visual amenity within that area. |
Article 4 Direction |
A legal instrument which extinguishes specific 'permitted development rights' from residential buildings within a defined area i.e. the right to do some types of minor works without planning permission. The effect of an article 4 direction is to require planning permission to be obtained from the Council before such work begins. Flats and commercial premises do not have permitted development rights so article 4 directions do not apply to them. |
Basin |
An area of land designed to retain storm runoff for a short period of time to reduce the risk of flooding and to allow the settlement of solids. These can be used as part of the implementation of a Sustainable Drainage System. |
Biodegradable Municipal Waste |
A type of waste, typically originating from plant or animal sources, which may be broken down by other living organisms. Also known as BMW. |
Biodiversity |
A measure of the variety of, and number of individuals within different species of plants, animals and other life forms that are present in a defined area. |
Blue Ribbon Network |
A spatial policy covering London's waterways and water spaces and the land alongside them. |
Building Regulations |
A statutory instrument made under powers provided in the Building Act 1984, and applying in England and Wales, which sets minimum construction standards for building works. The current edition of the regulations is 'The Building Regulations 2000' (as amended) and the majority of building projects are required to comply with them. They exist to ensure the health and safety of people in and around all types of buildings (i.e. domestic, commercial and industrial). They also provide for energy conservation, and access to and use of buildings. |
Building Schools for the Future |
A strategic approach to capital investment in school buildings to create the environment for the Government's agenda of educational transformation. |
Building at Risk |
A building identified in a Register kept by English Heritage of listed buildings as being in a poor or dilapidated condition or at risk from neglect or inappropriate changes. |
Central Activities Zone |
According to the London Plan the Central Activities Zone contains a unique cluster of vitally important activities including central government offices, headquarters and embassies, the largest concentration of London's financial and business services sector and the offices of trade, professional bodies, institutions, associations, associations, communications, publishing advertising and the media. |
Change of Use |
A change in the way that land or buildings are used (see Use Classes Order). Planning permission is usually necessary in order to change the use from one use class to another. |
Character |
The individual distinctiveness of an area, arising from a combination of natural and man-made elements with historic, socio-economic and other factors. |
Code for Sustainable Homes |
A document providing a single national standard to guide industry in the design and construction of sustainable homes. It is a means of driving continuous improvement, greater innovation and exemplary achievement in sustainable home building. The Code measures the sustainability of a home against design categories, rating the 'whole home' as a complete package. |
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) |
The combined production of heat, usually in the form of steam, and power, usually in the form of electricity. |
Commencement Order |
An instruction from the Secretary of State to the Local Planning Authority, requiring the authority to commence work on the preparation of its local development framework to replace its existing unitary development plan. |
Commission for Architecture and the Built Environment (CABE) |
The Government's advisor on architecture, urban design and public space. |
Community Infrastructure Levy |
The Community Infrastructure Levy (CIL) will be a new charge which local authorities in England and Wales will be empowered, but not required, to charge on most types of new development in their area. CIL charges will be based on simple formulae which relate the size of the charge to the size and character of the development paying it. The proceeds of the levy will be spent on local and sub-regional infrastructure to support the development of the area. |
Community Strategy |
A strategy document required by the Local Government Act 2000 to be prepared and implemented by a local planning authority with the aim of improving the social, environmental and economic well being of its area by co-ordinating the actions of local public, private, voluntary and community sectors. Responsibility for producing a community strategy may be passed to a local strategic partnership, which include local authority representatives. Also known as a Sustainable Community Strategy. |
Comparison Goods |
Retail items not bought on a frequent basis, for example televisions and white goods (fridges, dishwashers etc, and usually being the type of goods that people buy from the store offering the best value for money rather than the one closest to them. |
Conservation Area |
An area designated for the purpose of protecting the character of an area, and applied to areas of various sizes and characters, ranging from small groups of buildings to town squares or even open spaces. It may include one or more listed buildings. |
Conservation Area Character Appraisal |
A published document defining the special architectural or historic interest that warrants an area being designated as a conservation area. |
Contextual Indicators |
Contextual Indicators are intended to reflect the key characteristics and issues facing the borough and describe the wider, social, economic and environmental context in which the LDF policies operate. They provide a baseline position from which to develop LDF policies. |
Controlled Parking Zone |
An area of the public highway within which specified hours of parking control apply. Such controls do not apply to private roads. Also known as a CPZ. |
Convenience Goods |
Everyday essential household items, such as food. |
Core Output Indicators |
Output indicators assess the performance of LDF policies by measuring the quantifiable physical activities that are directly related to, and are a consequence of, the implementation of LDF policies. All planning authorities are required to monitor a set of core output indicators to provide a consistent data source to enable monitoring at the regional and national level. |
Core Policy |
A short clear statement of the matters which the local planning authority will take into account when it receives an application for planning permission. If the proposed development is not consistent with the policy, the local planning authority is likely to refuse planning permission unless there are exceptional circumstances affecting the site, which would make this particular development acceptable. Core Policies are set out in the Core Strategy. See also development management document for standards the Council will also take into account when determining planning applications. |
Core Strategy |
A Local Development Document setting out the long-term spatial vision and strategic objectives for the Local Planning Authority area. It includes a spatial strategy, core policies and a monitoring and implementation framework for achieving them. The Core Strategy has the status of a Development Plan Document. |
Decent Home |
A dwelling which:
|
Density |
A measure of the intensity of development of a plot of land. One measure of residential density is the number of habitable rooms per hectare (hrha). |
Density Matrix |
A residential development density control in the Further Alterations to the London Plan which seeks to achieve appropriate residential densities across London, based on the public transport accessibility level and character setting of the site and the characteristics of the scheme. |
Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform |
The Government department responsible for ensuring business success. It leads the Government's drive to raise UK levels of productivity, create the conditions for business success and strengthen the economic performance of all the regions. Previously known as the Department of Trade and Industry. |
Department for Communities and Local Government |
The Government department formed in 2006 to replace the Office of the Deputy Prime Minister. Also known as DCLG. |
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs |
The Government department responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in England. Also known as DEFRA. |
Department of Trade and Industry |
see Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform. Also known as DTI. |
Design and Access Statement |
Statements are documents that explain the design thinking behind a planning application. For example, they should show that the person applying for permission has thought carefully about how everyone, including disabled people, older people and very young children, will be able to use the places they want to build. |
Development Control/Management |
The process whereby a local planning authority receives and considers the merits of a planning application and whether it should be given permission, having regard to the development plan and all other material considerations. |
Development Management Document |
A document that sets out part or all a council's design standards for new developments. |
Development Plan |
A document that sets out policies and proposals for development and use of land and buildings within the area of a local planning authority. As set out in Section 38(6) of the Act, it consists of the relevant regional spatial strategy (or the spatial development strategy in the case of Greater London) and the development plan documents contained within its local development framework. |
Development Plan Document |
A spatial planning document that is subject to independent examination, and together with the relevant regional spatial strategy, forms the development plan for a local planning authority area for the purposes of the Act. It can be, but is not limited to, a core strategy, site schedule or area action plan (where needed). Also known as a DPD. DPDs are shown geographically on a proposals map. Individual DPDs or parts of a DPD can be reviewed independently from other DPDs. Each authority must set out the programme for preparing its DPDs in its local development scheme. |
District Centre |
A group of shops and some service outlets serving part of an urban area and providing a geographic focus for it, separate from and smaller than a major centre, but larger than and with more variety than local centres. |
Diversification |
The action of diversifying existing economic activity into new areas of business in order to broaden the return on capital or assets. |
Draft Replacement London Plan |
The Mayor of London has published a Draft Replacement London Plan for public consultation until 12 January 2010. It is intended that the Draft will undergo public examination in summer 2010 and be adopted towards the end of 2011. |
Early Alterations to the London Plan |
Alterations to the 2004 London Plan to address pressing housing provision, waste and minerals issues which underwent an independent examination in June 2006 and which were published in December 2006 and now form part of the London Plan. |
Education Authority |
A local government body responsible for providing education for pupils of school age in the area of that local government body. |
Energy Efficiency |
Using the minimum amount of energy needed to produce a given result. |
Enfield Design Guide |
A document to provide guidance on how development can be carried out in accordance with good design practice whilst retaining local distinctiveness (see Local Development Scheme for more details). |
Enfield Observatory |
An internet information portal developed by Enfield Council to provide easily accessible data, research and statistics about Enfield borough. |
Enfield Strategic Partnership |
The body which produced the community strategy "Enfield's Future" for Enfield borough. See also strategic partnership. |
English Heritage |
A Government advisory body with responsibility for all aspects of protecting and promoting the historic environment, and responsible for advising the Government on the listing of historic buildings (see listed building). |
Environment Agency |
A public body with responsibility for preventing or minimising the effects of pollution on the environment and which issues permits to monitor and control activities that handle or produce waste. It also provides up-to-date information on waste management and deals with other matters such as water issues, including flood protection advice. Also known as EA. |
Environmental Impact Assessment |
A procedure that must be followed in assessing the impact of certain types of development, usually more significant schemes, before they are granted planning permission. The procedure requires the developer to compile an Environmental Statement describing the likely significant effects of the development on the environment and proposed mitigation measures. |
Environment Statement |
A document required to be prepared as part of the preparation of an environmental impact assessment describing the likely significant effects of proposed development on the environment and proposed mitigation measures, and which must be circulated to statutory consultation bodies and made available to the public for comment. Its contents, together with any comments on it, must be taken into account by the competent authority (eg local planning authority) before it may grant consent. |
Equality Impact Assessment |
An Equality Impact Assessment examines a proposed or existing policy, plan, strategy or project to identify what effect its implementation may have on different groups in the community. It can anticipate and recommend ways to avoid any discriminatory or negative consequences for a particular group, and it also enables demonstration of the potential benefits for equality target groups arising from the proposed policy or project. |
Evidence Base |
The information and data gathered by a local authority to demonstrate the soundness of the policy approach set out in local development documents, and including assessment of the physical, economic, and social characteristics of an area. |
Examination-in-Public |
see Independent Examination |
Further Alterations to the London Plan |
Alterations to the 2004 London Plan introducing strategic regional policies which underwent an independent examination in June-July 2007 and which were published in February 2008 and which now form part of the London Plan. |
Generic Development Control/Management policies |
A suite of criteria-based policies the function of which is to ensure that all development within the area to which they apply meets the spatial vision and spatial objectives set out in the core strategy. They may be included in a development plan document or may form a stand-alone development plan document. |
Greater London Authority |
A strategic body constituted under the Greater London Authority Act 1999, consisting of the Mayor of London, the London Assembly and staff, which has responsibility for producing regional strategic policy in a numbers of areas, including transport, economic development, planning, and the environment for the county of Greater London. Also known as the GLA. It produces the London Plan. |
Greater London Authority Road Network |
see Transport for London Road Network |
Green Arc |
The GreenArc is a partnership of authorities, organisations and interest groups concerned with a wide stretch of countryside extending from north and east London to Bishops Stortford. |
Green Belt |
A designation for land around certain cities and large built-up areas, which aims to keep this land permanently open or largely undeveloped. Its purposes are to:
The detailed boundaries of such areas are defined in a development plan of each relevant local planning authority. |
Green Corridors |
Areas identified to promote environmentally sustainable forms of transport such as walking and cycling within urban areas and with the potential to act as vital linkages for wildlife dispersal between wetlands and the countryside. They can link housing areas to the national cycle network, town and city |
Green Grid Principles |
The Green Grid is a long term project to develop a network of open spaces and green links through Thames Gateway South Essex. |
Green Industry |
An environmentally friendly industry such as renewable energy and material processing and recycling facilities. |
Green Roofs |
Vegetated roofs, or roofs with vegetated spaces. Also known as eco-roofs. |
Growth Area |
An area identified for new residential development to accommodate population growth, as outlined in the Government's Sustainable Communities Plan and in the case of London including the Thames Gateway and the London-Stansted-Cambridge-Peterborough Corridor. |
Gypsy and Traveller |
Terms which in the context of planning and local authority law refers to anyone - regardless of race or origin - who is of a nomadic habit of life and who travels around for economic reasons, and includes but is not limited to:
|
Habitable Room |
A room within a dwelling house, but excluding kitchens less than 13 m2; bathrooms; toilets; sculleries not used for cooking; closets; pantries and storerooms; landings; halls; lobbies or recesses and offices or shops used solely for business purposes. |
Habitats Directive Assessment |
In accordance with the Habitats Directive 92/43/EEC the impacts of a land-use plan are assessed against the conservation objectives of a European Site, which includes Ramsar sites, and to ascertain whether it would adversely affect the integrity of that site. Also know as Appropriate Assessment. |
Health Impact Assessment |
A process for ensuring that land use and planning decision making at all levels consider the potential impacts of decisions on health and health inequalities. It identifies actions that can enhance positive effects and reduce or eliminate negative effects. |
Heritage Economic Regeneration Scheme |
An initiative launched by English Heritage in June 1998, planned to last for four years, and aimed at deprived areas which have not benefited from the various conservation led urban regeneration schemes of recent years, intended to positively involve business and communities, and with the primary objective of rescuing historic buildings at risk by achieving obvious heritage dividend in terms of benefits such as reuse of vacant upper floors, renewal of the economic base of areas and expansion of employment opportunities. Also known as HERS. |
Historic Parks and Gardens |
Parks and gardens included in a Register kept by English Heritage, ranging from town gardens and public parks to the great country estates, and reflecting the styles and tastes of past generations, from Medieval knot gardens and deer parks to sweeping 18th-century landscaped gardens, Victorian exotica and post-war examples. A local development plan can include a Register of Local Historic Parks and Gardens. |
Homes and Communities Agency (HCA) |
The Government's national housing and regeneration agency (formed as a result of a merger between the Housing Corporation and English Partnerships) that funds development of affordable housing, regulates registered social landlords and housing associations in England and and brings land back into productive use. |
House in Multiple Occupation |
Defined under the Housing Act 2004 as being:
Also known as HMO. |
Housing Association |
A not-for-profit body offering for rent independent homes owned by registered social landlords. |
Housing Demand |
The quantity of housing that households are willing and able to buy or rent. |
Housing Need |
The quantity of housing required for households who are unable to access suitable housing without financial assistance. |
Housing Tenure |
The financial and legal arrangements under which someone has the right to live in a house. The most frequent forms are tenancy, in which rent is paid to a landlord, and owner occupancy. Mixed forms of tenure are also possible. |
Independent |
A formal hearing, presided over by an Inspector or a Panel of Inspectors appointed by the Secretary of State, to consider the soundness of the development plan documents of a local planning authority or regional planning authority (eg the Greater London Authority). Also known as an Examination-in-Public (EiP). |
Index of Multiple Deprivation |
A ward-level index made up of six indicators (income, employment, health deprivation and disability, education, skills and training, housing and geographical access to services) for quantifying the degree of disadvantage in a ward, and which can help to identify areas for regeneration. Also known as IMD. |
IBP |
Commonly used throughout the Core Strategy as an acronym for Industrial Business Park. |
Infrastructure Delivery Plan |
The Infrastructure Delivery Plan sets out what social, physical and green infrastructure is required in the Borough to support planned growth in the Local Development Framework. The delivery of a soundLocal Development Framework is dependent on the Infrastructure Delivery Plan. |
Inspector's Report |
A report issued by the Inspector or Panel who conducted an independent examination, setting out their conclusions on the matters raised at the Examination and detailing the amendments which they require the Local Planning Authority to make to the Local Development Document before it adopts the document. The requirements of an Inspector's Report are binding. |
Intermediate Housing |
Housing at prices and rents above those of social rented housing, but below market price or rents, and which meet the criteria for affordable housing. These can include shared equity products (eg HomeBuy), other low cost homes for sale and intermediate rent. It can include homes provided by private sector bodies or provided without grant funding. Where such homes meet the definition of intermediate housing, they may be considered, for planning purposes, as affordable housing. Whereas, homes that do not meet this definition, for example, low cost market' housing, may not be considered, for planning purposes, as affordable housing. |
Issues and Options |
A document produced by a local planning authority during the early production stage of the preparation of Development Plan Documents and which may be issued for consultation to meet the requirements of Regulation 25 of the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004. |
Joint Waste Development Plan Document |
A document setting out the planning policies for waste management and identifying new and expanded waste facilities in North London. Also known as JWDPD. In the case of Enfield borough this document is usually referred to as the North London Waste Plan (NLWP). |
Key Worker |
A worker defined by the Government as being eligible by virtue of their type of employment for the purchase of housing provided by the Housing Corporation-funded Key WorkerLiving programme, and other workers employed in the public sector and not defined as a key worker but identified by the Regional Housing Board as eligible for the same housing purchase assistance. |
Land Registry |
The government agency responsible for the registration of title to land. Registration guarantees the title to land and therefore enables the sale of land and property to take place without needing to incur time and cost in checking through title deeds. |
Landfill Allowances Trading Scheme |
A Government initiative, implemented through DEFRA, designed to reduce the amount of biodegradable municipal waste sent to landfill. Also known as LATS. |
Lee Valley Corridor |
The area of strategically important development opportunities and existing industry either side of the River Lee, in parts of Enfield, Hackney, Haringey, Newham, Tower Hamlets and Waltham Forest boroughs. |
Lee Valley Regional Park |
A 4,000 ha (10,000 acre) regional park that stretches for 42 km (26 miles) on both sides of the River Lee, from the River Thames to Ware in Hertfordshire. |
Lee Valley Regional Park Authority |
A body constituted on 1 January 1967 under the Lee Valley Regional Park Act 1966 with responsibility for the Lee Valley Regional Park and for developing a wide range of leisure, sport and recreation, including nature conservation facilities and the protection and enhancement of the natural environment. |
Lifetime Homes |
Homes designed to meet the changing needs of the population from young children to the elderly, and thereby meeting the varying needs of numerous changes of occupiers in the same home by being designed to be accessible, adaptable and convenient and able to accommodate people with moderate mobility difficulties. |
Listed Building |
An historic building recorded on a statutory list of buildings of 'special architectural or historic interest' compiled by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990, on advice from English Heritage, to ensure that the architectural and historic interest of the building is carefully considered before any alterations, outside or inside, are agreed. A building is graded I, II* or II, with grade I being the highest. Listing includes the interior as well as the exterior of the building, and any buildings or permanent structures (e.g. wells) within the curtilage. |
Local Area Agreement |
Local Area Agreements set out the priorities for a local area agreed between central government and a local area and other key partners at the local level. |
Local Centre |
A small group of shops and limited service outlets serving a local catchment (for example, a suburban housing estate). Sometimes referred to as a neighbourhood centre. |
Local Development Document |
A document which forms part of the local development framework and which can be adopted and revised as a single entity and includes development plan documents, supplementary planning documents and the statement of community involvement. |
Local Development Framework |
A "folder" or suite of local development documents, drawn up by the local planning authority, which together with the relevant regional spatial strategy, and forms the development plan for its area. Also known as an LDF. |
Local Development Scheme |
A document setting out the intentions of the local planning authority for its local development framework; in particular, the local development documents it intends to produce and the timetable for their production and review. Also known as an LDS. |
Local Implementation Plan |
A statutory strategic transport plan produced by London boroughs bringing together transport proposals to implement the Mayor of London's Transport Strategy at the local level. Also known as an LIP |
Local Implementation Plan (HCA - Single Conversation) |
A document setting out the Council's long term resource requirements to deliver its Place Shaping vision and Housing Strategy objectives. This is part of the Single Conversation the Homes and Communities Agency's approach to placeshaping and delivery through partnership working. Also known as LIP |
Local List |
A list compiled by a local planning authority of buildings of special local architectural or historic interest but which do not meet the criteria to be statutorily listed by English Heritage as listed buildings. Councils are empowered by PPG 15 to draw up local lists and to support them through appropriate planning policies with the intention that, by drawing attention to the special interest of these buildings, owners will be encouraged to take particular care when undertaking any alterations or extensions. |
Locally Listed Building |
A building included on a local list. |
Local Output Indicators |
Planning authorities are also required to monitor local output indicators to address the outputs of any LDF policies not covered by the core output indicators. These will vary according to local circumstances and issues and will develop over time as the LDF is prepared. |
Local Planning Authority |
A body charged under the Act with the responsibility for preparing a local development framework for a specific area and for deciding whether development proposals should receive planning permission. In the case of Enfield Borough, Enfield Borough Council is the local planning authority. Also known as an LPA. |
Local Strategic Partnership |
A partnership of stakeholders which is usually non-statutory and multi-agency and which develops ways of involving local people from the public, private, community and voluntary sectors in the planning processes which shape the future of their neighbourhood and how services are provided, resulting in production of a community strategy. The Enfield Strategic Partnership is the local strategic partnership responsible for producing Enfield's community strategy. |
London Development Agency |
One of the Greater London Authority group organisations, acting on behalf of the Mayor of London, whose aim is to further the economic development and regeneration of London. Also known as the LDA. |
London Plan |
Also known as the Spatial Development Strategy, this document was published by the Mayor of London in February 2004 and provides a strategic framework for the boroughs' Unitary Development Plans. It will now perform this function in respect of Local Development Frameworks. It has the status of a development plan under the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act. There have been a number of alterations to the plan: Early Alterations to the London Plan, Further Alterations to the London Plan and the Minor Alteration to the London Plan. |
London-Stansted- Cambridge-Peterborough Corridor |
A land corridor covering the areas around and between North London, Harlow, Stansted Airport and Cambridge. Also known as the LSPC. It has been prioritised for development and growth by the Government in its Communities Plan ("Sustainable Communities: Building for the future"). |
Lower Super Output Area |
A Super Output Area (SOA) is a unit of geography used in the UK for statistical analysis. SOAs were created with the intention that they would not be subject to frequent boundary change. This makes SOAs more suitable to analyse statistical information figures than other geography units because they are less likely to change over time. Lower Layer Super Output Areas have an average population of 1,000 and are built from groups of Output Areas. |
LSIS |
Commonly used throughout the Core Strategy as an acronym for Locally Significant Industrial Sites. |
Major Centre |
Important shopping and service centres, often with a borough-wide or larger catchment. |
Market Housing |
Private housing for rent or for sale, where the price is set in the open market. |
Mayor of London |
An elected politician who heads the Greater London Authority and is responsible for budgeting and strategic planning of some governmental functions across the whole of the region of London. These include transport, police, fire and emergency services, economic development and regional spatial planning. |
Metropolitan Open Land |
Strategic open land within the urban area that contributes to the structure of London. Also known as MOL. |
Minor Alteration to the London Plan |
Alteration to the 2004 London Plan resulting from agreement between the Government Office for London, the Greater London Authority, London Councils and the Association of London Borough Planning Officers to apportion tonnages of municipal and commercial/industrial waste at London borough level (for management), as required by Planning Policy Statement 10 (PPS 10). This alteration was published in December 2006 and forms Table 4A.4 of the London Plan. |
Mixed Use Development |
Development for a variety of activities on single sites or across wider areas such as town centres and redundant industrial land. |
National Indicators |
The Government has introduced a set of streamlined indicators that reflect national priority outcomes for local planning authorities, which are the only measures on which central Government will performance manage outcomes delivered by local government working alone or in partnership. |
National Playing Fields Association |
A body charged with responsibility for ensuring that everyone has play, sport and recreation space close to where they live. |
Neighbourhood Renewal Fund |
A funding scheme to enable the councils of England's 88 most deprived local government areas, in collaboration with their Local Strategic Partnership, to improve services, to help narrow the gap between deprived areas and the rest of the country. |
Non Self Contained Accommodation |
Accommodation where occupants have the shared use of at least one of the following:
|
North London Chamber of Commerce |
A membership organisation run by business for business which represents the interests of business and commercial organisations. |
North London Strategic Alliance |
The sub-regional strategic partnership for North London established in 1999 which brings together public, private and voluntary organisations working in Barnet, Enfield, Haringey and Waltham Forest. Also known as NLSA. |
North London Sub-regional Development Framework |
The non-statutory framework providing guidance on Opportunity, Intensification and Regeneration Areas, town centres, suburbs and Strategic Employment Locations produced by the Mayor of London in partnership with boroughs and other stakeholders Also known as NLSRDF. |
North London Waste Authority |
Statutory waste disposal authority established in 1986 after the abolition of the Greater London Council to arrange the disposal of waste collected by its seven constituent boroughs: Barnet, Camden, Enfield, Hackney, Haringey, Islington and Waltham Forest. Also known as NLWA. |
North London Waste Plan |
see Joint Waste Development Plan Document |
Office for National Statistics |
The government agency which is the principal provider of official statistics about the UK. |
Office of the Deputy Prime Minister |
The Government department previously responsible for those functions undertaken by the Department for Communities and Local Government following its creation in 2006 |
Open Space |
All areas free of development. This includes space of public value, such as public landscaped areas, playing fields, parks and play areas, and also including areas of water such as rivers, canals, lakes and reservoirs, which can offer opportunities for sport and recreation or can also act as a visual amenity and a haven for wildlife. |
Opportunity Area |
One of a number of areas identified in the London Plan for accommodating large scale development to provide substantial numbers of new employment and housing, with a mixed and intensive use of land and assisted by good public transport accessibility. |
Outer London |
The Outer London boroughs are as follows: Barking and Dagenham, Barnet, Bexley, Brent, Bromley, Croydon, Ealing, Enfield, Haringey, Harrow, Havering, Hillingdon, Hounslow, Kingston upon Thames, Merton, Newham, Redbridge, Richmond upon Thames, Sutton, Waltham Forest. |
Outer London Commission |
A body established by the Mayor of London to advise how Outer London can play its full part in the city's economic success. |
Place Shaping |
A term created by Sir Michael Lyon in authoring "The Lyons Inquiry into Local Government" which advocates a more strategic role for local government and which is defined as: "the creative use of powers and influence to promote the general well-being of a community and its citizens". He states that this role should include the following:
|
Planning Policy Statement |
One of a range of documents which set out the Government's land use planning policies for England in respect of an aspect of planning and landuse. Also known as PPSs.Planning Policy Statements replace Planning Policy Guidance Notes as they are reviewed, and are issued by the Department for Communities and Local Government. |
Preferred options document |
One of the documents produced as part of the preparation of Development Plan Documents, and issued for formal public participation. |
PIL |
Commonly used throughout the Core Strategy as an acronym for Preferred Industrial Location. |
Primary Capital Programme |
A national scheme that aims to develop primary schools and primary age special schools across the country. |
Primary Care Trust |
Statutory body responsible for delivering health care and health improvements to its local area. Also known as PCT and NHS Enfield. |
Primary Shopping Frontage |
An area where retailing and the number of shops in a major centre or district centre is most concentrated. |
Proposals Map |
A local development document which comprises a map of the local planning authority's area, and is the spatial representation of the authority's adopted development plan, showing:
|
Public Realm |
Areas that are accessible to everyone (whether publicly or privately owned). In urban areas, this includes most streets, squares and parks. |
Public Transport Accessibility Level |
A quantified measure of the extent and ease of access by public transport to facilities and services, and the degree of access to the public transport network. Also known as PTAL. |
Ramsar Sites |
Ramsar sites are wetlands of international importance, designated under the Ramsar Convention. |
Reasoned Justification |
A summary of the local planning authority's reasons for including a particular core policy within the core strategy. |
Regional Spatial Strategy |
A document prepared by a regional spatial planning authority setting out the authority's policies in relation to the development and use of land and forming part of the regional development plan for local planning authorities. |
Registered Social Landlord |
Independent not-for-profit provider of housing, registered with the Housing Corporation under the Housing Act 1996. Also known as an RSL. An RSL may be an Industrial and Provident Societies, a registered charity or a company. |
Renewable Energy |
Energy derived from sources that can be replenished at the rate at which they are used. For example, energy derived from sustainably farmed trees, the wind, water flow, tides or the sun. |
Residential Care Home |
An establishment which provides personal care assistance to its residents, such as dressing and washing, where staff can also care for residents during short periods of illness. |
Rugg Review |
A review, commissioned by the Government in January 2008, to look at what problems landlords and tenants face in the private rented sector. |
Saved policy or plan |
A unitary development plan or a part or parts of a unitary development plan which is exempted from a general order rescinding the plan or a class or classes of provisions of such plans. Enfield's adopted unitary development plan was saved (continued in force) automatically for three years from the date of commencement of the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act in 2004. At the expiry of this period in 2007 the Enfield UDP policies were required to undergo an assessment to assess their appropriateness for saving beyond this time period until such time as the UDP was replaced by the LDF. As a result of this assessment most of Enfield's unitary development plan policies were saved whilst fifty-three expired in September 2007. |
Scheduled Ancient Monument |
A nationally important site or monuments given legal protection by being placed on a list (schedule). In England, English Heritage is responsible for identifying appropriate sites that are then officially scheduled by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport. |
Secondary Shopping Frontage |
A retailing area, secondary to the primary shopping frontage, that provides greater opportunities for a diversity of uses. |
Section 106 Agreement |
A legal agreement under Section 106 of the Town & Country Planning Act 1990 between a planning authority and a developer, in order to achieve the aims of relevant planning policies through ensuring that certain extra works related to a development are undertaken. |
Sheltered Housing |
A form of housing provision which offers a range of services to help people to live independently with the added security of having someone to call on in emergencies and different from other housing because a scheme manager or warden lives on the premises or nearby. Some schemes are designed specifically for people with disabilities and may have specialised facilities and specially trained staff to provide care. |
SIL |
Commonly used throughout the Core Strategy as an acronym for Strategic Industrial Land. |
Significant Effects Indicators |
Significant effects indicators assess the significant social, environmental and economic effects of policies and inform the monitoring of the impact of policies on sustainability. Government guidance requires that these significant effects indicators should be selected to link to the SA objectives and indicators and then monitoring should enable a comparison to be made between the predicted effects and actual effects measured during implementation of the policies. |
Site of Borough Importance for Nature Conservation |
A site which contains a significant example at borough level of a natural habitat which contains particularly species or assemblages of species which are rare in the borough or which contain important populations of species, or which is of particular significance within otherwise heavily built-up areas of London. |
Site of Importance for Nature Conservation |
A site originally identified by the Greater London Council, or later by the London Ecology Unit, London boroughs or Greater London Authority, chosen to represent the most significant wildlife habitats and emphasise the value of access for people. Also known as a SINC. SINCs are classified into sites of metropolitan, borough and local importance for nature conservation. |
Site of Local Importance for Nature Conservation |
A site of importance for nature conservation which is, or may be, of particular value to people nearby (such as residents or schools) and is particularly important in areas otherwise deficient in nearby wildlife sites, as determined by the GLA. Only those sites that provide a significant contribution to the ecology of a local area are defined as sites of local importance. |
Site of Metropolitan Importance for Nature Conservation |
A site which contains a significant example of a natural London habitat which contains particularly rare species, rare assemblages of species or important populations of species, or which is of particular significance within otherwise heavily built-up areas of London. Also known as a SMINC. SMINCs are of the highest priority for protection. |
Site of Special Scientific Interest |
A site identified under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 (as amended by the Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000) as an area of special interest by reason of any of its flora, fauna, geological or physiographical features (basically, plants, animals, and natural features relating to the Earth's structure). Also known as an SSSI. |
Sites Schedule |
A development plan document setting out the allocations of sites for specific uses/developments. |
Small and Medium sized Enterprise |
An independent business managed by its owner or part owners and having a small market share either by number of employees or turnover. Also known as a SME. |
Social Exclusion |
A term for the result of people or areas suffer from a combination of linked problems, such as unemployment, poor skills, low incomes, poor housing, high crime environments, bad health and family breakdown. |
Social Infrastructure |
Covers facilities such as health provision, early years provision, schools, colleges and universities, community, cultural, recreation and sports facilities, places of worship, policing and other criminal justice or community safety facilities, children and young people's play and informal recreation facilities. This list is not intended to be exhaustive and other facilities can be included as social infrastructure. |
Social Rented Housing |
Rented housing owned and managed by local authorities and registered social landlords, for which guideline target rents are determined through the national rent regime. It may also include rented housing owned or managed by other persons and provided under equivalent rental arrangements to the above, as agreed with the local authority or with the Housing Corporation as a condition of grant. |
Soundness |
See test of soundness |
Spatial Development Strategy |
see regional spatial strategy |
Spatial Planning |
An ongoing process of managing change which goes beyond traditional land use planning to bring together and integrate policies for the development and use of land with other policies and programmes which influence the nature of places and how they function. This includes policies which can affect land use by influencing the demands on, or needs for, development, but which are not capable of being delivered solely or mainly through the granting or refusal of planning permission and which may be implemented by other means. |
Spatial Portrait |
A succinct description of the area, designed to portray its individual character, key trends and the current 'drivers for change'. |
Statement of Community Involvement |
A document which sets out the standards that a local planning authority will achieve with regard to involving local communities in the preparation of Local Development Documents and development control decisions, and which is not a Development Plan Document but is subject to independent examination. |
Strategic Employment Location |
One of a number of locations defined in the London Plan, and identified as a Preferred Industrial Location, Industrial Business Park or Science Park, the existence of which helps to ensure that sufficient sites of appropriate quality and attributes in appropriate locations are provided to meet the needs of the general business, industrial and warehousing sectors. Also known as an SEL. |
Strategic Environmental Assessment |
A generic term used to describe environmental assessment as applied to policies, plans and programmes. European 'SEA Directive'(2001/42/EC) requires a formal 'environmental assessment of certain plans and programmes, including those in the field of planning and land use'. It is a tool for integrating environmental considerations into decision-making by ensuring that any significant environmental effects of the decision are taken into account, and must form an integral part of the adoption process for Local Development Documents and must be taken into account right from the initial stages of plan preparation. Also known as an SEA. |
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment (SFRA) |
Local planning authorities (LPA) are required to undertake a Strategic Flood Risk Assessment (SFRA) as part of the planning process in accordance PPS25. SFRAs provide information about flood risk throughout the area of the LPA, either individually or combined with neighbouring LPAs. The SFRA will consider the effects of climate change on river and coastal flooding, identify the risk from other sources of flooding, and consider appropriate policies for development in or adjacent to flood risk areas. |
Strategic Partnership |
A co-operative arrangement set up to bring together major public sector organisations, local businesses, community and voluntary groups, to create a healthy, prosperous, cohesive community living in a borough that is safe, clean and green and responsible for producing a Community Strategy. |
Strategic Road Network |
see Transport for London Road Network |
Subdivision |
The division of a lot, tract, or parcel of land into two or more lots. |
Submission DPD |
A stage in the statutory process for the adoption of local development documents that are also development plan documents. The local planning authority must submit the draft DPD, known as the submission DPD,to the Secretary of State for independent examination. |
Supplementary Planning Document |
A local development document providing supplementary information in respect of the policies in development plan documents and not forming part of the development plan nor subject to independent examination. Instead the local planning authority can approve the document by formal resolution of the Council, but it must be subjected to full public consultation if it is to be accorded any weight in decisions on development proposals. Also known as an SPD. |
Sustainability Appraisal |
The examination of a local development document to ascertain whether its policies and proposals reflect sustainable development objectives (i.e. social, environmental and economic factors). Also known as an SA. |
Sustainable Community Strategy |
see Community Strategy |
Sustainable |
A community which achieves the objectives set out in the Government's "Sustainable Communities: Building for the Future":
|
Sustainable Design and Construction |
A philosophy of creating buildings that meet the needs of building users and the wider community and minimises environmental impact by:
|
Sustainable Development |
The core principle underpinning contemporary town planning in the UK, based on the ideal of ensuring a better quality of life through development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The Government has set out four aims for sustainable development:
These aims should be pursued in an integrated way through a sustainable, innovative and productive economy that delivers high levels of employment, and a just society that promotes social inclusion, sustainable communities and personal well being, in ways that protect and enhance the physical environment and optimise resource and energy use. |
Sustainability |
see Sustainable Development |
Sustainable Drainage System |
Also known as SUDs. SUDS deal with run-off as close to its source as possible and balance all three objectives, rather than focusing only on flood prevention. Two examples are Swales and basins which retain water for a period of time prior to discharge to a natural watercourse. SUDs are one of a number measures to manage flood risk. |
Swale |
A type of sustainable drainage system which consists of a grassed depression which lead surface water overland from the drained surface to a storage or discharge system, typically using the green space of a roadside margin. |
Test of Soundness |
The testing of a Development Plan Document in terms of being based on good evidence and being prepared in accordance with all the necessary procedures including measures set out in the relevant Statement of Community Involvement. The full list of tests against which documents are assessed is set out in Planning Policy Statement 12. |
Thames Gateway |
The area comprising a corridor of land on either side of the Thames extending eastwards from Deptford Creek and the Royal Docks to Sheerness in Kent and Southend-on-Sea in Essex, with the part within London including parts of the lower end of the Lee Valley around Stratford. It includes parts of the boroughs of Barking & Dagenham, Bexley, Greenwich, Havering, Lewisham, Newham and Tower Hamlets as well as limited parts of Hackney and Waltham Forest. |
Thameslink |
A new National Rail cross-London link between Bedford and Brighton building on the existing Farringdon-Blackfriars line. |
Third Sector |
A term used to describe the collection of non-governmental organisations that are value driven and principally reinvest their surpluses to further social, environmental or cultural objectives. This includes voluntary and community organisations, charities, social enterprises, cooperatives and mutuals and housing associations. |
Topography |
A description (or visual representation on a map) of the shape of the land, for example, contours or changes in the height of land relative to sea level. |
Townscape |
The general appearance of a built-up area, for example a street, a town or city. |
Transport Assessment |
An assessment of the availability of, and levels of access to, all forms of transportation from a site. |
Transport for London |
One of the GLA group organisations, accountable to the Mayor of London, with responsibility for delivering an integrated and sustainable transport strategy and operation for London. Also known as TfL. |
Transport for London Road Network |
The mayor's term for the Greater London Authority Road Network as described in the Greater London Authority Act 1999 and comprising 550 km of London's red routes and other important streets. Also known as the TLRN. |
Traveller |
see Gypsy and Traveller |
Unitary Development Plan |
A type of development plan introduced in 1986 and replaced by local development frameworks in the Act. Enfield's unitary development plan was adopted in March 1994. Also known as a UDP. |
Upper Lee Valley Opportunity Area |
see Opportunity Area |
Urban Design |
The design of buildings, groups of buildings, spaces and landscapes, in villages, towns and cities, to create successful development. |
Urban Grain |
The pattern, size and arrangement of street blocks and plots. |
Use Class |
A category of landuse activities requiring planning permission which is set according to a use classes order. The uses are grouped into classes A, B, C and D and sui generis (a use not within a specific class). The classes are: Al (shops); A2 (financial and professional services); A3 (restaurants and cafes); A4 (drinking establishments); AS (hot food takeaways); B1 (business); B2 (general industry); B8 (storage and distribution); Cl (hotels); C2 (residential institutions); C2A (secure residential institutions); C3 (dwelling houses); D1 (non-residential institutions); D2 (assembly and leisure); Sui Generis (a use not within a specific class). |
Use Classes Order |
A legislative mechanism under the terms of the Town and Country Planning Act 1990, as amended by the Use Classes (Amendment) Order 2005, and the General Permitted Development (Amendment) Order 2005, which sets out when permission is or is not required for changes to the use of land and buildings, and the circumstances under which such changes can be undertaken. |
West Anglia Route Modernisation Enhancements |
A project designed to provide significant capacity and other performance improvements on the London-Stansted-Cambridge-Peterborough rail route. Also known as WARME. |
Wider Determinants of Health |
A wide range of factors which contribute to the health of individuals, including:
|
1 Where this column is blank the 1994 UDP Policies saved in 2007 under Section 38 of Planning & Compulsory Purchase Act remain valid. An indication is provided in this table as to which forthcoming LDF Document is likely to supersede or formally expire remaining UDP policies. Each new LDF Policy Document will provide a similar appendix to update on superseded or expired UDP policies.
2 Core Strategy preparation has been subject to an Equalities Impact Assessment
3 Addressed in section 4.1 Spatial Strategy
4 Article 4 Directions are addressed in national policy
5 General development considerations are addressed by national policy
6 General development considerations are addressed by national policy
7 General development considerations are addressed by national policy
8 General development considerations are addressed by national policy