
14.1 There is no statutory requirement for the impact of the Neighbourhood Plan and its policies to be monitored.
14.2 Portland Town Council will monitor the impact of policies on change in the neighbourhood area by considering the policies’:
14.3 The Town Council will keep a record of planning applications, any applicable policies, and comments from the Town Council together with the eventual outcome of the application. The Town Council will establish data-gathering systems, such as those relating to local housing need and second home ownership, to help inform development decisions and monitor change. The Town Council will liaise regularly with community bodies, such as the Portland Community Partnership, to share information and feedback on planning-related matters.
14.4 A full or partial review of the Portland Neighbourhood Plan may be triggered by changes to legislation, changes to national or district-wide planning policies, or significant planning issues being raised by the local community that cannot be dealt with effectively by a combination of national, district and/or existing neighbourhood plan policies. Five years from the date the Plan is made, we will consider the need and value in undertaking a full Review.
Affordable Housing - housing for sale or rent, for those whose needs are not met by the market (including housing that provides a subsidised route to home ownership and/or is for essential local workers); and which complies with one of the various definitions of affordable housing in the NPPF61.
Aquaculture - the farming of fish, shellfish and other aquatic organisms.
Biodiversity - The variety of life in all forms e.g. wildlife, plants, etc.
Brownfield Site - Previously developed land which is or was occupied by a permanent structure, including the curtilage of the developed land and any associated fixed surface infrastructure.
Community Land Trust - is a form of community-led housing, set up and run by ordinary people to develop and manage homes as well as other assets important to that community, like community enterprises, food growing or workspaces. CLTs act as long-term stewards of housing, ensuring that it remains genuinely affordable, based on what people actually earn in their area, not just for now but for every future occupier.
Conservation Area - An area of special architectural or historic interest, designated under the Planning (Listed Buildings & Conservation Areas) Act 1991, whose character and appearance it is desirable to preserve and enhance. There are special rules on some development in conservation areas.
European Sites - This is a site protected for its importance to biodiversity. They are defined in Regulation 8 of the Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations 2010 and include candidate Special Areas of Conservation, Sites of Community Importance, Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas.
Flood Risk Assessment - An assessment of the likelihood of flooding in an area so that development need and mitigation measures can be carefully considered.
Green Infrastructure - A network of multi-functional green space, urban and rural, which is capable of delivering a wide range of environmental and quality of life benefits for local communities.
Habitat Regulations Assessment (HRA) - A HRA is a requirement of European Directive 92/43/EEC which assesses the potential effects a local development plan may have on one or more European sites (Natura 2000 sites). The assessment should conclude whether or not a proposal or policy in a development plan would adversely affect the integrity of the site in question.
Heritage Asset - A building, monument, site, place, area or landscape identified as having a degree of significance meriting consideration in planning decisions, because of its heritage interest. Heritage asset includes designated heritage assets and assets identified by the local planning authority (including local listing).
Infrastructure - Basic services necessary for development to take place, for example, roads, electricity, sewerage, water, education and health facilities.
Landscape Character – The distinct and recognisable pattern of elements that occur consistently in a particular type of landscape. It reflects particular combinations of geology, landform, soils, vegetation, land use and human settlement.
Listed Buildings - A building of special architectural or historic interest. Listed buildings are graded I, II* or II; with grade I the highest. Listing includes the interior as well as the exterior of the building, and any buildings or permanent structures (e.g. wells within its curtilage). English Heritage is responsible for designating buildings for listing in England.
Local Education Authority - The public body whose duty it is to carry out specific functions relating to education for a defined area. All references to local education authority apply in this Plan to Dorset Council.
Local Green Space - Green areas of importance to local communities designated to provide special protection against development.
Local Nature Reserve - Non-statutory habitats of local significance designated by local authorities where protection and public understanding of nature conservation is encouraged.
Local Plan - A plan for the future development of a local area, drawn up by the local planning authority in consultation with the community. In law this is described as the development plan documents adopted under the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004. A local plan can consist of either strategic or non-strategic policies, or a combination of the two.
Local Planning Authority - The public body whose duty it is to carry out specific planning functions for a defined area. All references to local planning authority apply in this Plan to Dorset Council.
Major Development - For housing, development is where 10 or more homes will be provided, or the site has an area of 0.5 hectares or more. For non-residential development it means additional floorspace of 1,000m2 or more, or a site of 1 hectare or more, or as otherwise provided in the Town and Country Planning (Development Management Procedure) (England) Order 2015. (This is the NPPF definition.)
Minerals Plan - A statutory development plan prepared by a minerals’ planning authority (Dorset Council) setting out policies for the control of development constituting of the winning and working of minerals or the deposit of mineral waste.
Natura 2000 Network - The European network of protected sites established under the Birds Directive and the Habitats Directive (SACs and SPAs – see elsewhere in this Glossary).
Neighbourhood Plan - A plan prepared by a Town or Parish Council or Neighbourhood Forum for a neighbourhood area (made under the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004).
NPPF - The National Planning Policy Framework sets out the Government's planning policies for England and how these are expected to be applied. It sets out the Government's requirements for the planning system only to the extent that it is relevant, proportionate and necessary to do so. It provides a framework within which local people and their accountable councils can produce their own distinctive local and neighbourhood plans, which reflect the needs and priorities of communities.
PPG - The National Planning Practice Guidance is a web-based resource which brings together planning guidance on various topics into one place. It was launched in March 2014 and coincided with the cancelling of most of the Government Circulars which had previously given guidance on many aspects of planning.
Permitted Development - Permission to carry out certain limited forms of development without the need to make an application to a local planning authority, as granted under the terms of the Town and Country Planning (General Permitted Development) Order.
Previously Developed Land - is that which is or was occupied by a permanent structure (excluding agricultural or forestry buildings) and associated fixed‐surface infrastructure. The definition covers the curtilage of the development.
Principal Residence - residences occupied as the residents' sole or main residence, where the residents spend the majority of their time when not working away from home.
Public Arts - Permanent or temporary physical works of art visible to the public, whether part of a building or free-standing. For example, sculpture, lighting effects, street furniture, paving, railings and signs.
Public Realm – are those parts of a village, town or city (whether publicly or privately owned) available, for everyone to use. This includes streets, squares and parks.
Public Right of Way is a highway over which the public have a right of access along the route.
Ramsar Site - A wetland of international importance, protected under the Ramsar Convention on the
sustainable use and conservation of Wetlands.
Renewable Energy - is energy flows that occur naturally and repeatedly in the environment, for example from the wind, water flow, tides or the sun.
Registered Social Landlord – is a technical name for a body registered with the Housing Corporation. Most Housing Associations are RSLs.
Second Home - is a property that is furnished but no-one’s sole or main residence.
Scheduled Monument - is an historic building or site that is included in the Schedule of Monuments kept by the Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
SHMA - A Strategic Housing Market Assessment is a study of the way the housing market works in an area. It considers the type of households living in the area, where they work and what sort of housing they live in. It attempts to estimate future housing needs across the area, broken down by tenure and size of housing.
Shoreline Management Plan - a non-statutory document that provides a broad assessment of the long-term risks associated with coastal processes.
SNCI Site of Nature Conservation Importance - Locally important sites of nature conservation adopted by local authorities for planning purposes.
Special Area of Conservation (SAC) - A site of Community importance designated by the Member States where the necessary conservation measures are applied for the measurement or restoration, at a favourable conservation status, of the habitats and or species for which the site is designated.
Special Protection Area (SPA) - A site designated under the Birds Directive by the Member States where appropriate steps are taken to protect the bird species for which the site is designated.
SSSI - A Site of Special Scientific Interest identified under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 (as amended by the Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000) as an area of special interest by reason of any of its flora, fauna, geological or physiographical features (basically, plants, animals, and natural features relating to the Earth's structure).
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) – is a procedure (set out in the Environmental Assessment of Plans and Programmes Regulations 2004) which requires the formal environmental assessment of certain plans and programmes which are likely to have significant effects on the environment.
SUDS - is a concept that makes environmental quality and people a priority in drainage design, construction and maintenance. The sustainable drainage system (SUDS) approach includes measures to prevent pollution, reduce surface water runoff at source and provide a range of physical structures designed to receive the runoff.
Supplementary Planning Document (SPD) - Documents which add further detail to the policies in the Local Plan. They can be used to provide further guidance for development on specific sites or issues, such as design. Supplementary planning documents are capable of being a material consideration in planning decisions but are not part of the development plan.
Transport Impact Assessment - considers the impact of a proposed development on all modes of transport and requires developers to consider ways to reduce the number of private car journeys and increase the use of more sustainable modes, to their development.
Transport Interchange Point - at which transfer between types of (modes) transport may take place.
Use Class Order - The Town and Country Planning (Use Classes) Order 1987 puts uses of land and buildings into various categories. Planning permission is not needed for changes of use within the same use class.
Waste Plan - A statutory development plan prepared (or saved) by the waste planning authority (Dorset Council) setting out policies in relation to waste management and related developments.
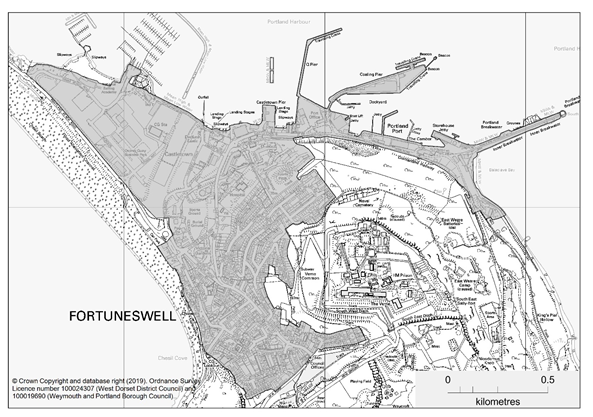
Fortuneswell / Castletown DDB
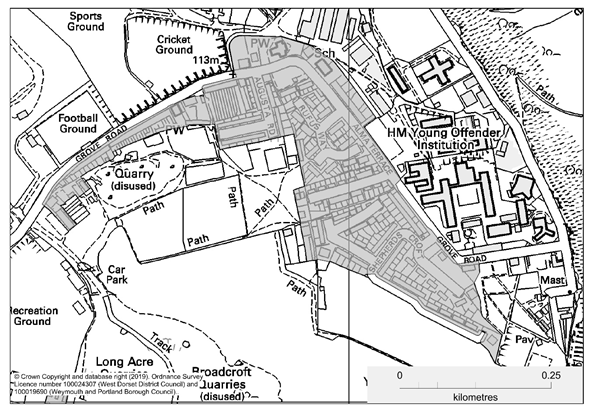
The Grove DDB
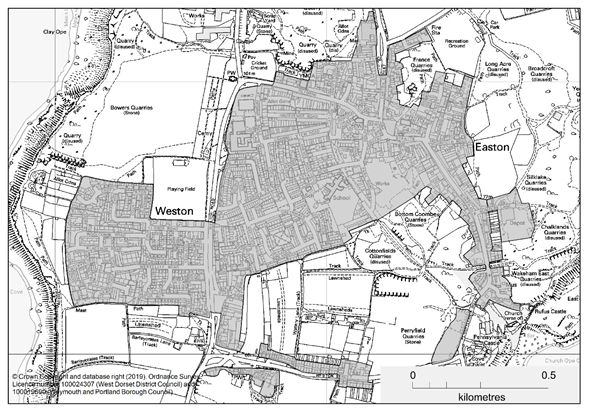
Weston / Easton DDB
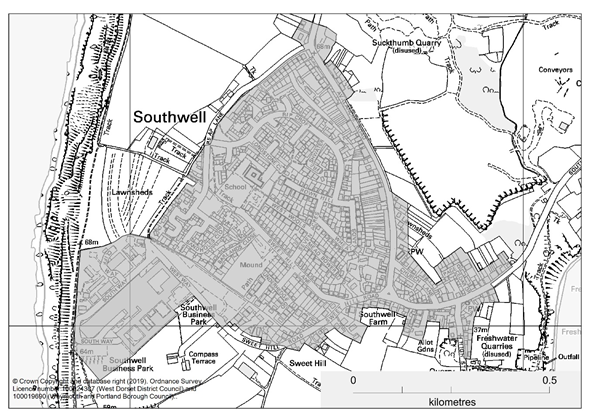
Southwell DDB
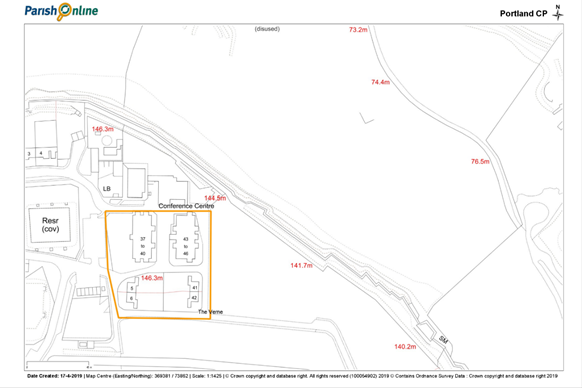
The Verne Policy Area
Key Employment Areas - protected under Policy ECON2 of the Local Plan
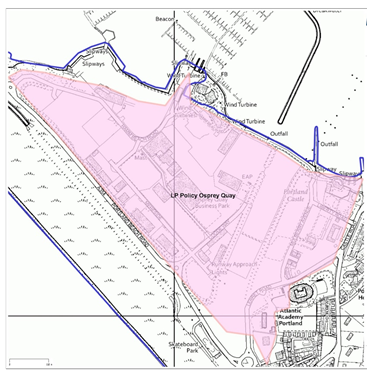
Osprey Quay
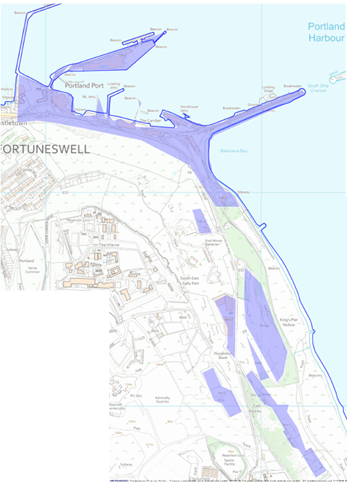
Portland North
Portland Central
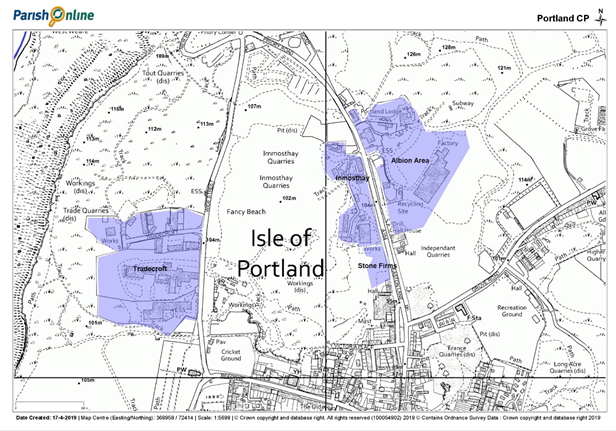
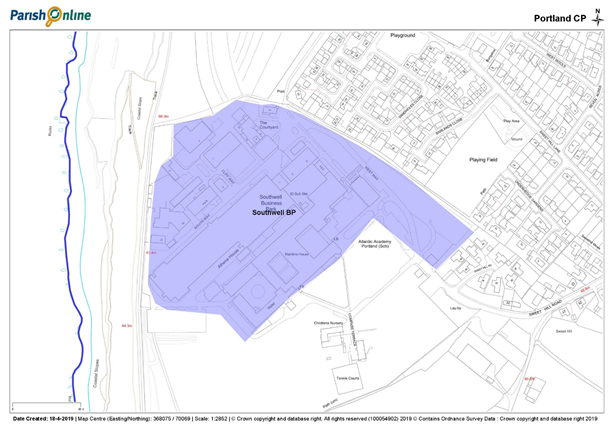
Southwell Business Park
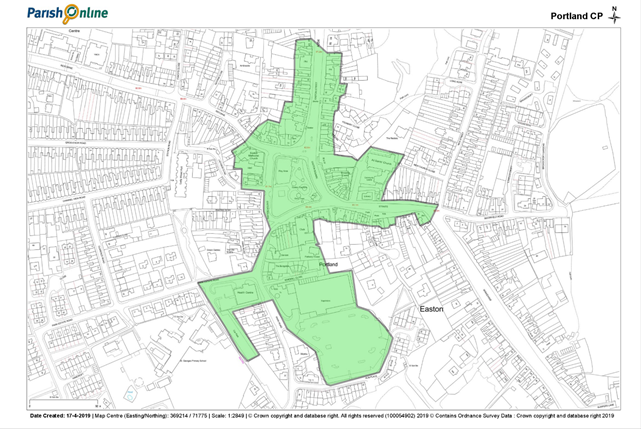
Easton Local Centre
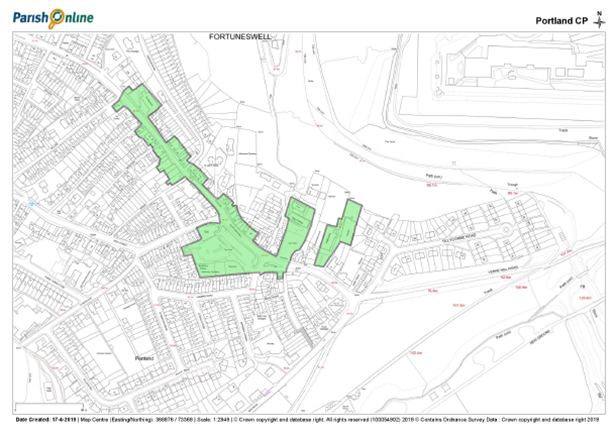
Fortuneswell Local Centre
Chiswell Neighbourhood Centre
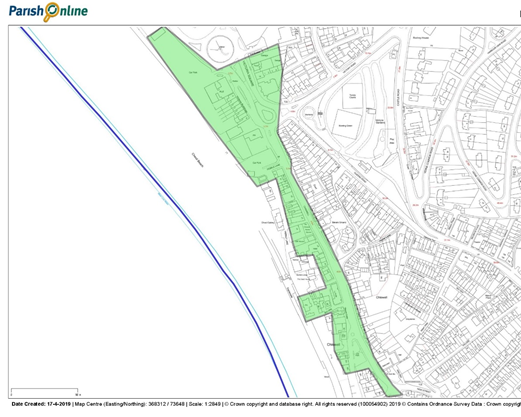
Castletown Neighbourhood Centre
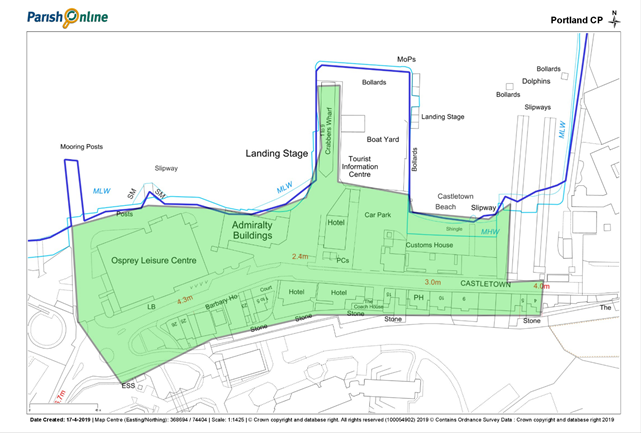
Fortuneswell / Castletown area Local Green Spaces
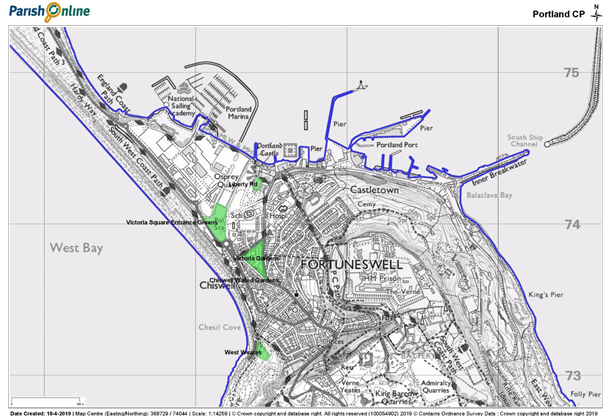
The Grove area Local Green Spaces
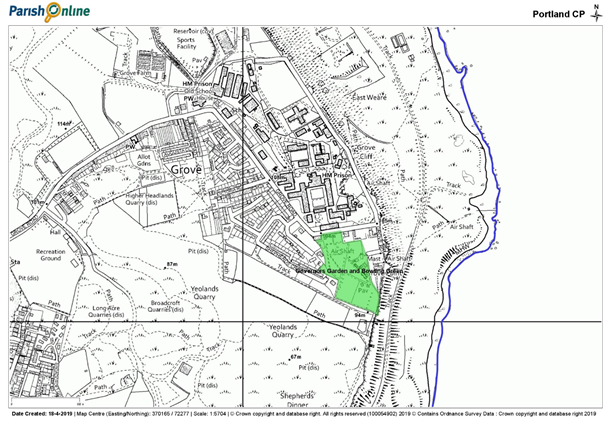
Weston and Easton area Local Green Spaces
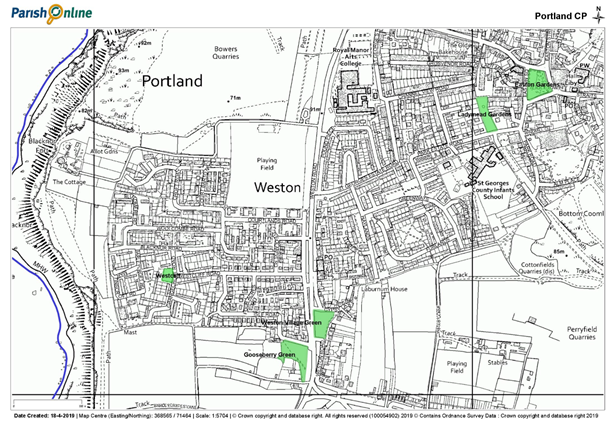
Southwell area Local Green Spaces
61 See NPPF Glossary https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/728643/Revised_NPPF_2018.pdf